Wood chips, bamboo chips and rice husks and other industrial and agricultural processing waste, usually burned as fuel, even if used to make activated carbon can only use medicine to produce powdered activated carbon. The method uses the waste material to produce granular activated carbon through extrusion molding, crushing, carbonization, activation and other processes, which not only expands the application range, but also can be reused many times. The process is as follows:
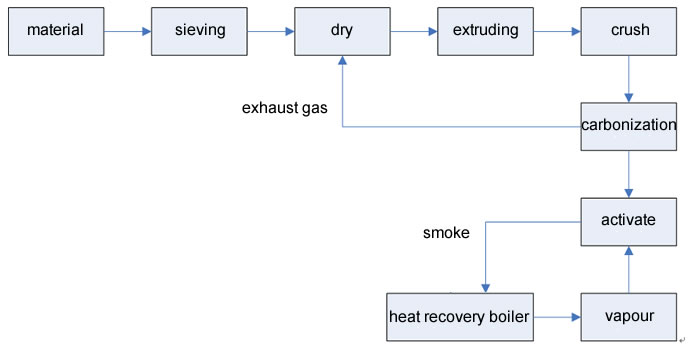
As can be seen from the chart, according to this process, the entire production process does not require any additional fuel, which is an energy-saving production line; because it does not need a coal-fired boiler, there is no SOX and NOX emissions, so it is a good environmental production line; since energy costs are saved, production costs also follow suit, so it is also a profitable production line. Example 1: Taiwanese wood chips (mainly composed of a single component) are dried (moisture content ≤22%) at 150°C-220°C and pressed into shape at 150°C-220°C. They are carbonized at 550±50°C and activated at 850±50°C. The adsorption indicators of activated carbon are: iodine value ≥1100mg/g; methylene blue dye removal capacity ≥180mg/g. Example 2: Chinese wood chips (with more complex composition) are treated in the same way as Example 1, with the adsorption indicators of activated carbon being: iodine value ≥1050mg/g; methylene blue dye removal capacity ≥165mg/g. Official website: www.vikenton.com Example 3: Bamboo chips, treated in the same process, have finished products with adsorption indicators of: iodine value ≥1100mg/g; methylene blue dye removal capacity ≥200mg/g.

